Advanced Energy Modeling Techniques for Complex Infrastructure
Exploring cutting-edge energy modeling methodologies that improve accuracy and enable better decision-making for large-scale infrastructure projects.
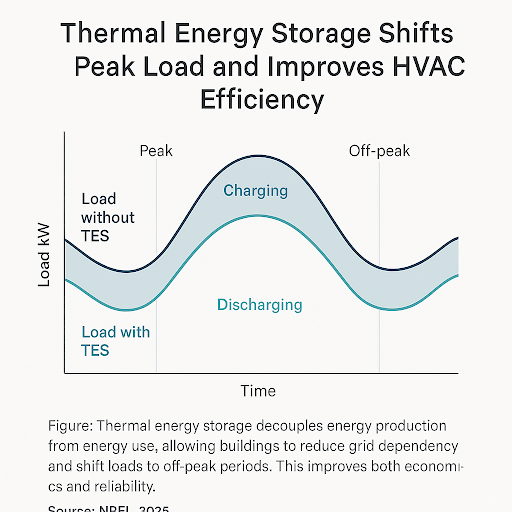
Advanced Energy Modeling: Rethinking Infrastructure from the Ground Up
Modern infrastructure isn't just steel and concrete anymore—it's a living, breathing system of data-driven energy flows, unpredictable behavior patterns, and increasingly complex design targets. That's where traditional energy modeling hits its limit. And it's exactly why we're seeing a shift—a full-blown evolution—toward advanced energy modeling techniques built for today's complexity.
Why Traditional Energy Modeling Falls Short
You've probably seen it: static models with generic assumptions. They're fine for checking a box—but they collapse when asked to predict performance in interconnected systems where occupant behavior, variable loads, and changing weather overlap. These models often miss the mark entirely on lifecycle impact or performance under nonstandard conditions like part-load or shoulder seasons.
So what's the fix? We don't need more assumptions—we need resolution. Granularity. Dynamic simulation.
The Stack: Techniques Driving Next-Gen Modeling
Let's walk through the tech stack redefining energy modeling:
1. Parametric Modeling
Instead of guessing at what works, parametric modeling allows us to systematically test everything. Building orientation? Window-to-wall ratios? Thermal mass? All tweakable. Using defined variables and relationships, we run thousands of simulations automatically—surfacing energy-saving geometries, envelope strategies, and passive design tactics in early design phases.
Result? Optimal performance, minimal material waste.
2. Digital Twins
This is the feedback loop we've always needed. Real-time sensor data feeds into a virtual clone of the building. We see how systems behave under actual operating conditions—not just theoretical ones. Digital twins allow us to spot inefficiencies in real-time, run predictive simulations using neural networks (LSTM, CNN, ANN), and proactively maintain HVAC and lighting systems.
Bonus: It bridges the gap between Building Information Modeling (BIM) and operational analytics.
3. AI and Machine Learning
We're not just modeling airflow or heat gain—we're learning from patterns. Deep reinforcement learning is being used to control HVAC in real time. Model Predictive Control (MPC) powered by deep learning can slash energy use by up to 50% without sacrificing thermal comfort (PNNL, 2024).
Need to predict next week's load? Or optimize how to use on-site batteries? AI's got that.
4. BIM + BEM Integration
No more redundant data entry or siloed workflows. When BIM data flows directly into energy modeling software, designers can assess the impact of envelope materials, HVAC configurations, and shading systems—all before a shovel hits the ground.
This seamless integration reduces design-time errors, improves model fidelity, and accelerates compliance with certifications like LEED or BREEAM.
5. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
Want to know where your thermal stratification is killing HVAC performance? Or where stale air pools? CFD gives us a pixel-by-pixel map of air velocity, temperature, and humidity. PMV and DR indexes can be calculated with pinpoint precision—critical for healthcare, data centers, and high-performance commercial spaces.
Here's what it looks like in practice:

Figure: CFD simulation of air temperature gradients in a naturally ventilated space. Zones of discomfort and energy waste can be identified and mitigated before construction begins.
Case in Point: Real-World Wins
Warehouse Retrofit:
- Combined CFD and energy modeling cut AHU count in half—$1.3M in CapEx saved, plus $80k in annual OPEX reductions.
Digital Twin in Operations:
- Office tower in Toronto used IoT-integrated digital twins to optimize chiller sequencing—resulting in a 23% cut in peak demand.
AI-Driven Controls:
- Commercial tower in Boston trained a deep reinforcement learning agent to control HVAC—cut consumption by 48% compared to baseline reactive logic.
But… There's Friction
Let's be honest—this stuff isn't plug-and-play.
- Computational cost is non-trivial. CFD and parametric runs eat up hours, if not days, without high-performance computing.
- Software interoperability is still messy. BIM to BEM workflows require constant tweaking.
- Validation is everything. You can't trust models until you've calibrated them against real-world utility data.
- Skilled talent remains a bottleneck. These tools demand deep understanding of thermodynamics, systems engineering, and data analytics.
The Payoff: Why It's Worth It
Still, when done right, advanced energy modeling pays for itself. Early simulations can unlock up to 45% energy savings compared to business-as-usual design (NY Engineers, 2024). Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA) becomes 10x more accurate. And real-time optimization with digital twins ensures operational performance doesn't drift off-spec after commissioning.

Figure: Average savings over building lifespan when energy modeling is integrated in conceptual vs. late design stages.
The Bottom Line
We're not guessing anymore. We're simulating, optimizing, validating—and redefining what infrastructure performance means.
The combination of parametric design, machine learning, digital twins, and CFD is not just better—it's necessary. And with growing regulatory pressure, energy costs, and emissions targets, waiting to upgrade our modeling methods just isn't an option.
Related Articles
Exploring how advanced heat pump systems are revolutionizing district energy networks and enabling low-carbon heating and cooling solutions.
An in-depth look at the design and implementation of the 51,000 MBH heat pump district heating plant and its impact on urban sustainability.